通常,可再生能源既有積極的一面,也有消極的一面。它們之所以出色,是因?yàn)檫@些資源中的大多數(shù)在世界范圍內(nèi)廣泛分布,因?yàn)樗鼈儙缀醪粫?huì)耗盡,并且因?yàn)槠涫褂貌粫?huì)破壞環(huán)境。它們不會(huì)產(chǎn)生大量電能,而且大多數(shù)可再生資源都容易隨時(shí)間變化,這是其負(fù)面影響的一部分。
對(duì)于大多數(shù)可再生能源,有必要在重要地區(qū)(太陽(yáng)能或風(fēng)能發(fā)電站)安裝電廠,這需要大量的建筑材料和大量的資金,即使由于費(fèi)用低廉而花費(fèi)了很多時(shí)間開發(fā)。
由于這些原因,可再生能源的使用是一個(gè)需要很多考慮和準(zhǔn)確性的問題。
·永不耗盡
使用化石燃料(例如煤,天然氣或石油產(chǎn)品)的發(fā)電廠在很大程度上取決于這些物質(zhì)的供應(yīng)。危險(xiǎn)不僅在于供應(yīng)突然中斷,還在于燃料價(jià)格突然上漲。例如,1970年代的燃料危機(jī)迫使電力運(yùn)輸和替代能源的發(fā)展。
地球核心的熱量幾乎不會(huì)耗盡。核心溫度約為6,000°C。無(wú)需擔(dān)心人類會(huì)以任何方式影響這一點(diǎn)。
·穩(wěn)定
太陽(yáng)能和風(fēng)能取決于天氣狀況。沒有風(fēng)或沒有陽(yáng)光,就意味著沒有生產(chǎn),站會(huì)把它們儲(chǔ)存在蓄能器中的東西散發(fā)出去。儲(chǔ)存此能量的電池容量有限。如果無(wú)風(fēng)或無(wú)陽(yáng)光的天氣持續(xù)很長(zhǎng)時(shí)間,則一段時(shí)間內(nèi)將不會(huì)有電。
核心會(huì)產(chǎn)生大量的24/7熱量。井井有條的發(fā)電站可以正常運(yùn)行,并且在任何天氣,白天或夜晚,任何季節(jié)都可以發(fā)電。
·電站所需面積較小
向基礎(chǔ)設(shè)施很少或很少的偏遠(yuǎn)地區(qū)供電一直是一個(gè)問題。缺乏適當(dāng)?shù)膶掗煹缆罚鹆昊蛏絽^(qū)景觀-這些都是阻礙傳統(tǒng)發(fā)電廠創(chuàng)建的重大障礙。
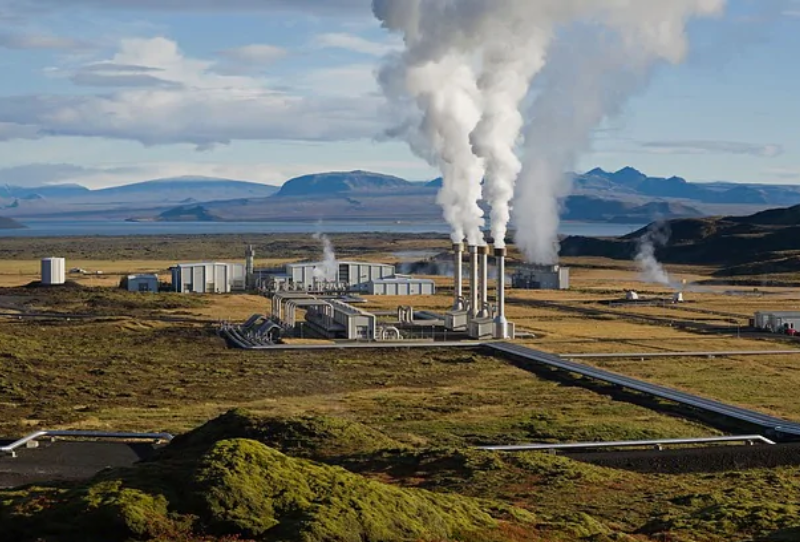
地?zé)?/a>能最重要的優(yōu)勢(shì)之一就是幾乎在任何地方都可以使用。熱源實(shí)際上位于地下。地上部分僅由帶有渦輪機(jī)和發(fā)電機(jī)的機(jī)房以及冷卻塔組成。與適當(dāng)?shù)?a href=/topic/1533.html target=_blank>太陽(yáng)能發(fā)電廠所需的廣闊領(lǐng)域相比,它們?cè)谝黄鹚璧目臻g很小。
· 環(huán)保
與以大量CO2污染大氣而聞名的傳統(tǒng)發(fā)電站相比,地球核心的熱量產(chǎn)生的能量非常干凈。只有核電廠釋放的二氧化碳更少。但是,他們的問題在于放射性廢物。
· 允許礦物提取
取決于區(qū)域,來(lái)自地下并旋轉(zhuǎn)渦輪的蒸汽可能包含各種氣體和礦物質(zhì)。例如,在意大利,蒸汽帶走了大量的硼酸溶液。
如前所述,使渦輪旋轉(zhuǎn)的蒸汽可能包含多種溶液,氣體和礦物質(zhì)。來(lái)自地下深處的蒸汽不是用飲用水制成的。它包含站點(diǎn)所在的地殼特定部分所特有的元素。這些元素和化合物可能包含鉛,鎘,砷,硫,鋅,氨,苯酚等。如果此類解決方案到達(dá)當(dāng)?shù)亓饔颍瑒t會(huì)造成環(huán)境災(zāi)難。
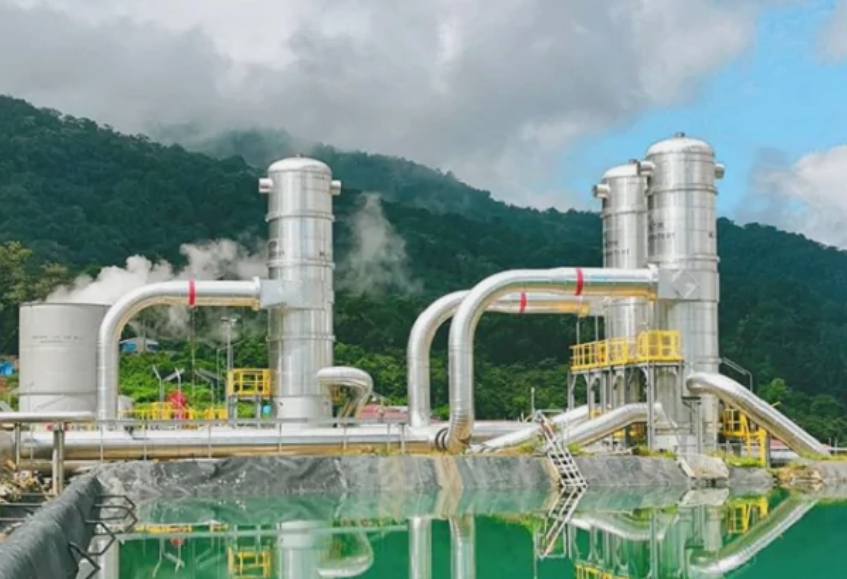

正確遵守所有安全措施后,進(jìn)入大氣的蒸汽會(huì)通過特殊的過濾器。冷凝水及其所有溶液被倒回鉆孔中。但是,在不可抗力的情況下,這樣的站點(diǎn)會(huì)損害生物圈。
·巨額預(yù)付款
建筑物的成本是地?zé)?/a>能最大的弊端之一。盡管構(gòu)造相對(duì)簡(jiǎn)單,但這種發(fā)電廠在建造階段卻相當(dāng)昂貴。它需要對(duì)位置,其浮雕和地下巖層進(jìn)行徹底的分析和調(diào)查。由于必須打深井才能達(dá)到所需溫度,因此孔的深度也可能影響成本。
·生產(chǎn)率相對(duì)較低
目前,地?zé)?/a>發(fā)電廠的發(fā)電量少于水力發(fā)電站,核電站或普通熱電廠。許多鉆孔只能釋放出足夠的能量,僅用于小規(guī)模的沉降。
有必要比較地?zé)?/a>能的利弊,看看哪一個(gè)會(huì)比另一個(gè)更重要。目前,許多國(guó)家都存在利用堆芯熱量的發(fā)電站。他們的能力足以滿足一部分人口的用電需求。
其余的由傳統(tǒng)的火力,核能或水力發(fā)電站提供。這樣的站在地震活動(dòng)頻繁的地區(qū)非常有效。最好的例子是冰島,地殼的厚度使植物比其他國(guó)家更容易到達(dá)地球內(nèi)部的熱量。
在冰島和日本,深層供暖的數(shù)量可直接用于道路,衣服和民居的加熱。薩爾瓦多的全部電源供應(yīng)中約25%來(lái)自地球核心的熱量。
為了促進(jìn)可再生能源的使用,應(yīng)徹底評(píng)估地?zé)?/a>能的利弊。從化石燃料的消耗速度來(lái)看,不久之后,人類將需要轉(zhuǎn)向可再生能源。地?zé)?/a>能將成為未來(lái)的理想能源存儲(chǔ)。
Geothermal Energy Pros And Cons
Evelyn Bankole Alternative methods of producing electricity – from waves, wind, solar radiation, or the warmth of the Earth’s core – are thought to be our future. Still, geothermal energy pros and cons are a very hot talking point in expert circles. Environmentally friendly and quite efficient, this method of producing power has a range of significant advantages and drawbacks that need thorough consideration.

Geothermal energy advantages and disadvantages explained
Renewable sources of energy, in general, have a range of both positive and negative sides. They are great because the majority of these sources are widely spread around the world, because they will hardly ever run out, and because their usage does not ruin the environment. The fact that they do not produce a lot of power and that most renewable sources are prone to change with time are some of its negative aspects.
For most renewable power sources, it is necessary to install power plants on significant territories (solar or wind stations), and this requires plenty of building materials and a lot of money, even though the expenses are covered with time due to the low cost of exploitation.
For these reasons, the usage of renewable sources of energy is a question that requires much consideration and accuracy.
The main advantages of geothermal energy
·It never runs out
Power plants that use fossil fuel like coal, gas or oil products depend significantly on the supply of these substances. The danger is not only in an abrupt break in the supply but also in a sudden increase in prices for the fuel. For example, the fuel crisis in the 1970s forced the development of electrical transport and alternative energy sources.
The heat of the Earth’s core will hardly ever run out. The temperature of the core is about 6,000°C. There is no need to worry that humanity can influence this in any way.
·It is stable
Solar and wind energy depend on weather conditions. No wind or no sunlight means that there is no production, and stations give away what they have stored in accumulators. The batteries that store this energy have a limited capacity. If windless or sunless weather last for a long time, there will be no electricity in a while.
The core produces plenty of heat 24/7. An adequately organized power station can function without breakdowns and produce electricity in any weather, day or night, any season.
·Power stations require relatively small territories
Supplying electricity to remote regions which have no or little infrastructure has always been a problem. Lack of proper wide roads, a hilly or mountainous landscape – these are big obstacles that hinder the creation of traditional power plants.
One of the most significant geothermal energy advantages is its availability practically everywhere. The source of heat lies literally under the ground. The above-ground part consists of only a machinery room with a turbine and a generator, and a cooling tower. Together, they require little space compared to the vast fields required for a proper solar plant.
·It is environmentally friendly
Compared to traditional powerhouses that are known for polluting the atmosphere with a lot of CO2, the energy produced by the heat of the Earth’s core is quite clean. Only nuclear power plants give off less CO2; their problem, however, is in radioactive waste.
·It allows mineral extraction
Depending on the region, the steam that comes from under the ground to rotate turbines can contain various gases and minerals. For example, in Italy, the steam brings up solutions of boric acid in significant quantities.
The major disadvantages of geothermal energy
As it was just mentioned above, the steam that rotates turbines may contain a range of solutions, gases, and minerals. The steam that comes from underground depths is not made of potable water. It contains elements that are characteristic for the particular part of the Earth’s crust where the station is located. These elements and compounds may consist of lead, cadmium, arsenic, sulfur, zinc, ammonia, phenol, and much more. If such solutions reach local water basins, it can cause an environmental catastrophe.

When all safety measures are correctly observed, the steam that goes into the atmosphere passes through special filters. The condensed water with all its solutions is poured back into the borehole. In the case of force majeure, though, such a station can harm the biosphere.
·Huge upfront bills
The cost of the building is one of the biggest cons of geothermal energy. In spite of the relatively simple construction, such a power plant turns out to be rather costly at the building stage. It requires a thorough analysis and investigation of the location, its relief, and underground formations. Since it is necessary to bore a deep well to reach the point of the required temperature, the depth of the hole may also influence the cost.
·Productivity is relatively low
At present, geothermal power plants produce less electricity than hydroelectric stations, nuclear power plants or usual thermal stations. Many boreholes can give off energy enough for small settlements only.
It is necessary to compare the pros and cons of geothermal energy and see which will outweigh the other. At the moment, power stations that use the heat of the core exist in many countries. Their capacity is enough to cover a part of the population’s needs for electricity.
Traditional thermal, nuclear or hydropower stations supply the rest. Such stations are very effective in areas of high seismic activity. The best example is Iceland where the thickness of the crust allows the plants to reach the inner Earth's heat much easier than in other countries.
In Iceland and Japan, the heat of the depth is available in such quantities that it is used directly to heat roads, clothes, and people's homes. About 25% of the entire power supply in El Salvador comes from the heat of the Earth's core.
Geothermal energy pros and cons should be thoroughly evaluated for the sake of promoting the usage of renewable energy. Judging by how quickly fossil fuel is being spent, quite soon, humanity will need to switch to renewable sources of energy. Geothermal power will work as the perfect storage of energy for the future.